Example 2: from a square to a bubble¶
Files¶
- Comprehensive test file: main.cpp
- Reference results for comparison: time_specialized.csv
Statement of the problem¶
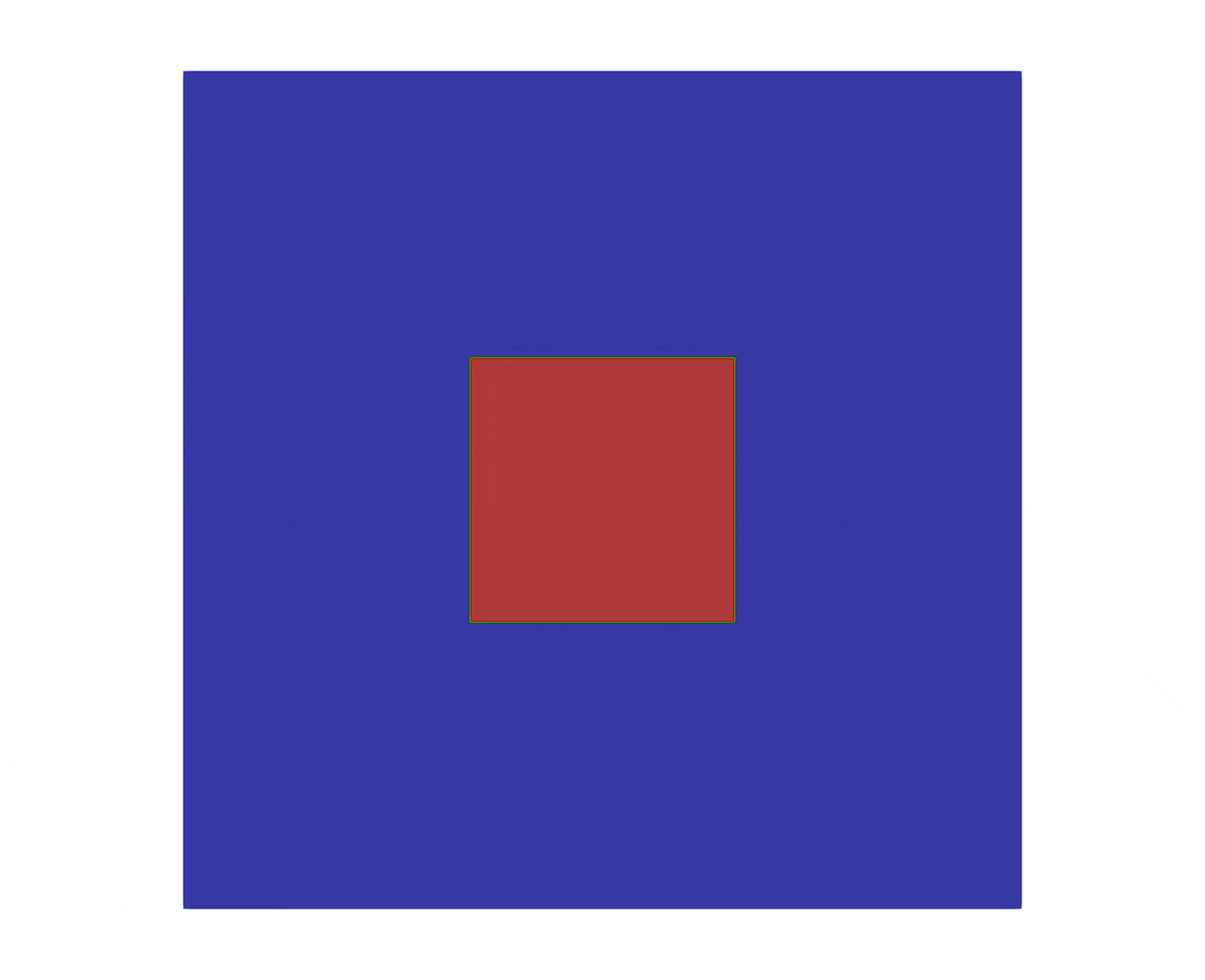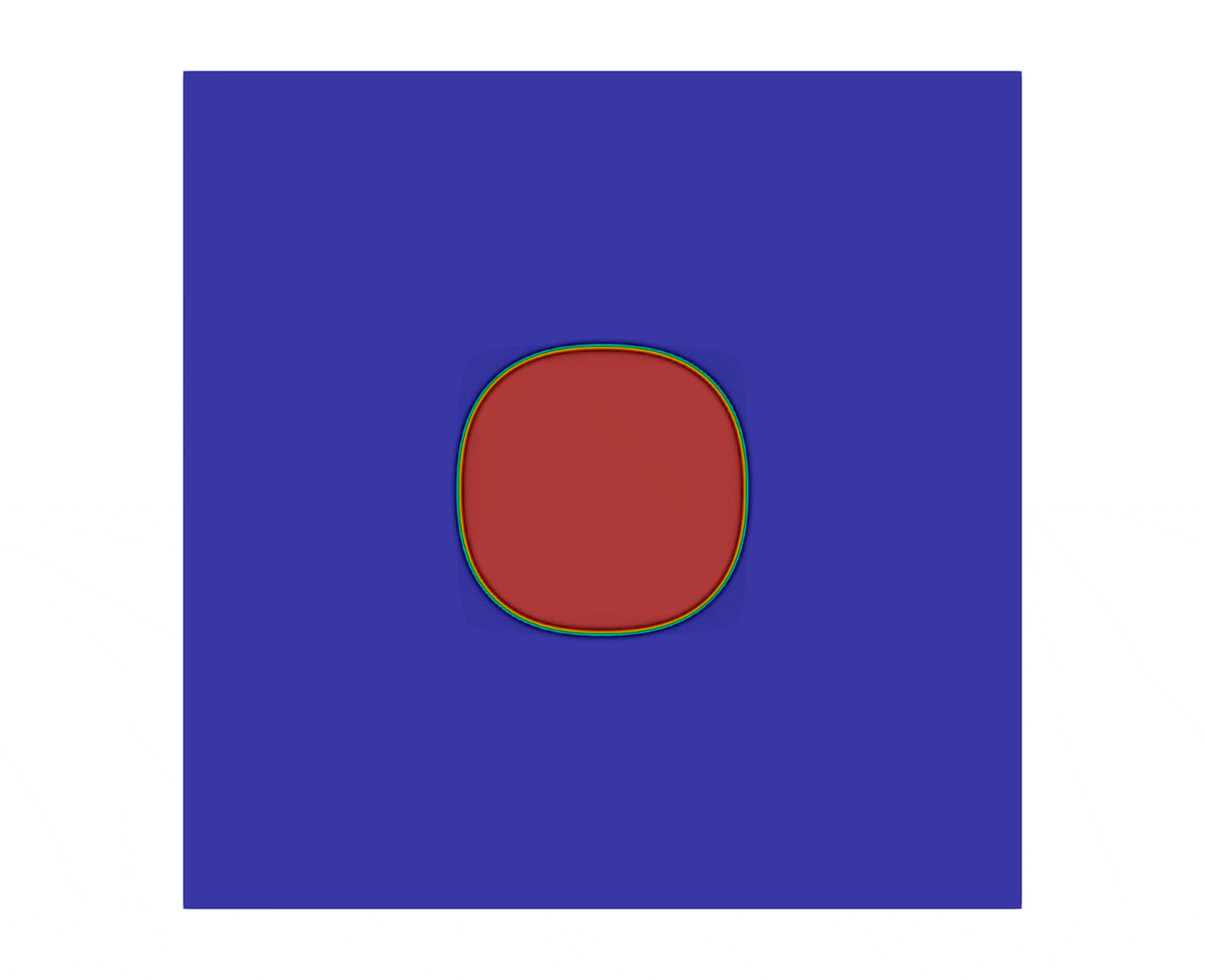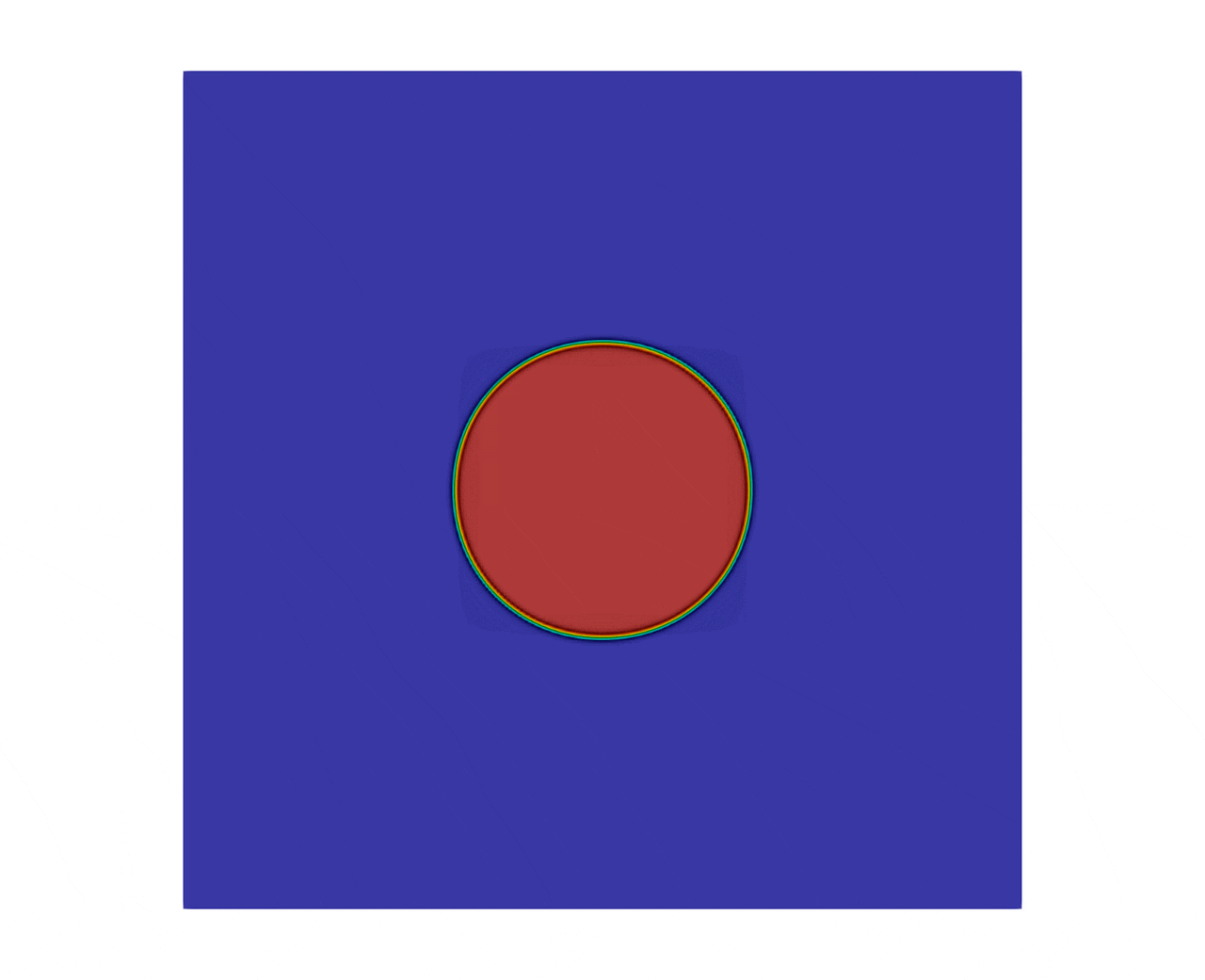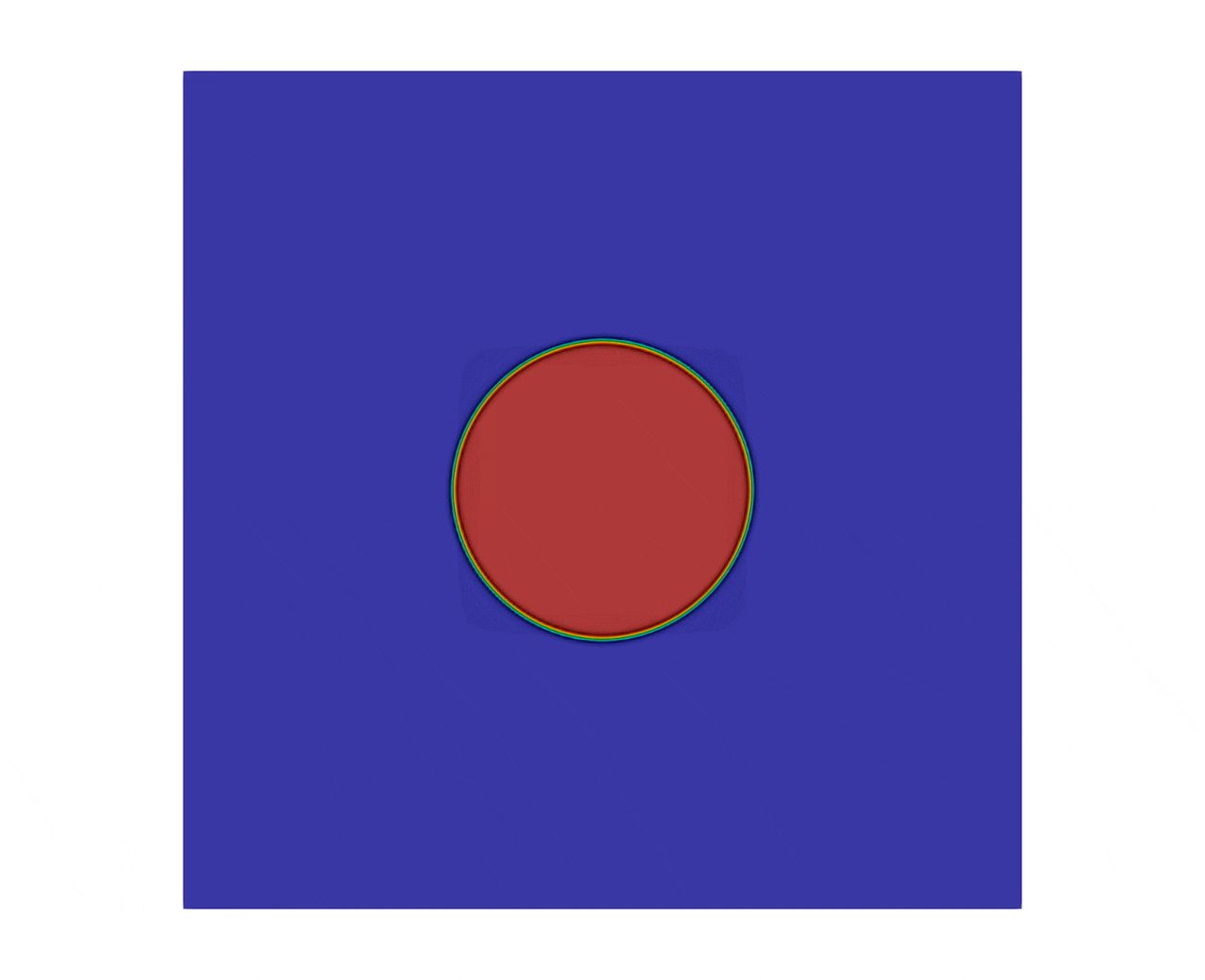
This test corresponds to a 2D simulation of a square evolving to a bubble.
The domain is a square
where is the phase indicator, the generalized chemical potential and the derivative against of the potential defined by:
Initial condition¶
The initial condition consists of square:
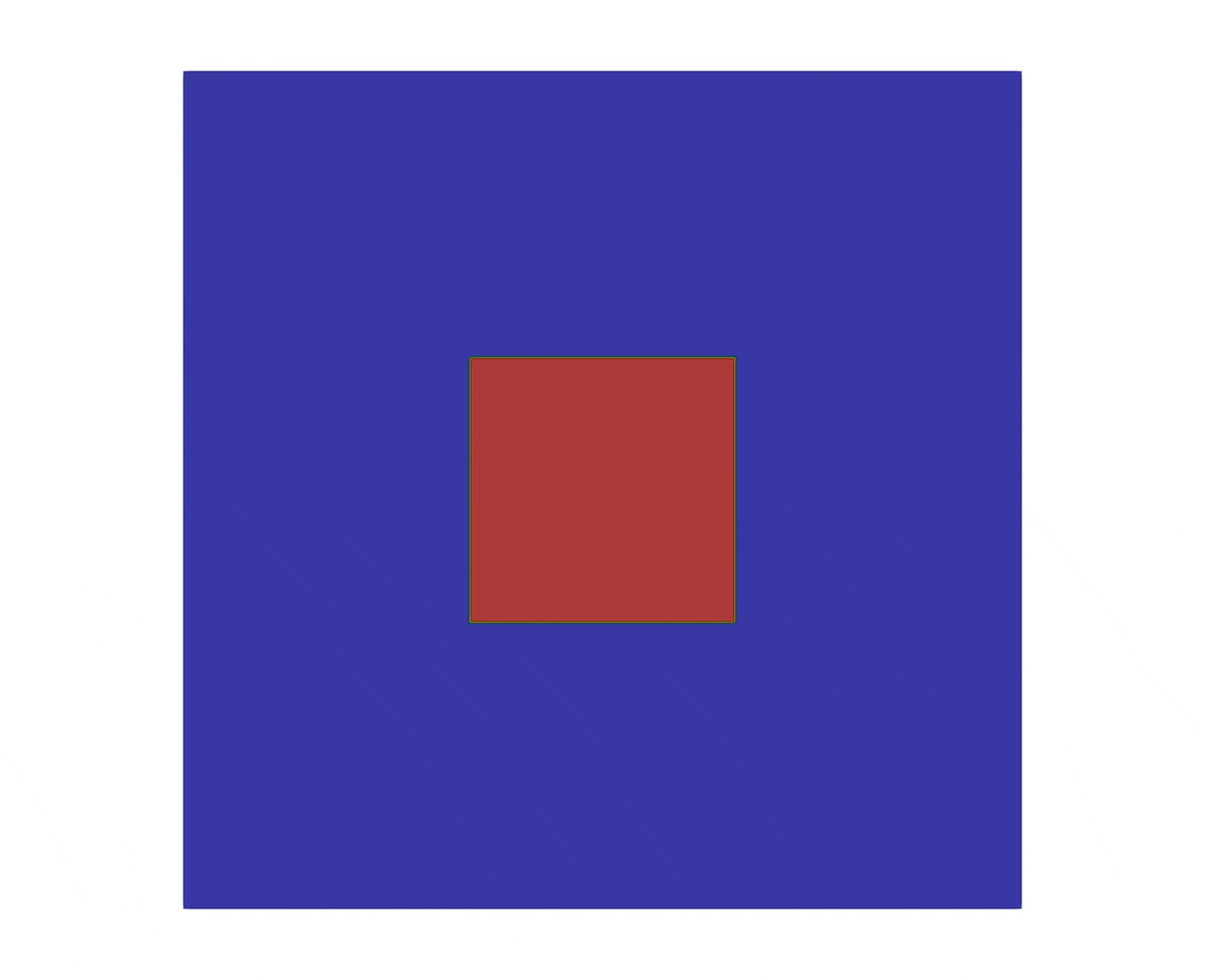
Parameters used for the test¶
For this test, all parameters are equal to one except the energy gradient coefficient.
| Name | Description | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
mob |
mobility coefficient | ||
lambda |
energy gradient coefficient | ||
omega |
depth of the double-well potential |
Boundary conditions¶
Neumann boundary conditions are prescribed on the boundary of the domain:
Numerical scheme¶
- Time integration: Euler Implicit over the interval (it could be extended further) with a time-step
- Spatial discretization: uniform grid with nodes in each spatial direction
- Newton solver: relative tolerance , absolute tolerance
- Iterative solver: HYPRE_GMRES
- Preconditioner: HYPRE_ILU
Results¶
The average value of is an available ouput of the simulation (see the file time_specialized.csv). It is defined by:
For this test, the computed average value should remain constant over time.
The figure 2 shows the evolution of a square to a bubble, with a final simulation time set to .